Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate among nutritionists, researchers, and food enthusiasts alike. While it’s recognized that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it’s crucial to understand the nuances of sugar addiction in the context of our modern diet. The effects of sugar on our brain and behavior can feel similar to those seen with more traditionally addictive substances, often leading to sugar cravings especially in the face of highly processed food addiction. Yet, unlike alcohol or drugs, sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance according to clinical criteria, prompting discussions about the addictive qualities of sugar and the consequences of overconsumption.
When discussing the concept of sugar addiction, one might consider various terms such as sweet substance dependency or the habitual consumption of sugary foods. The allure of sweet flavors often leads individuals to seek out sugary snacks and beverages, reflecting a growing concern over processed food habits. While sugar can enhance the taste and enjoyment of meals, the prevalence of sugar cravings in our food-laden environment raises essential questions about dietary habits and health. Understanding the psychological and physiological responses to sweet foods can provide insights into how we manage our cravings and develop healthier eating practices. Ultimately, while sugar offers pleasure and satisfaction, its potential for dependency warrants attention in our ongoing conversations about nutrition and wellness.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
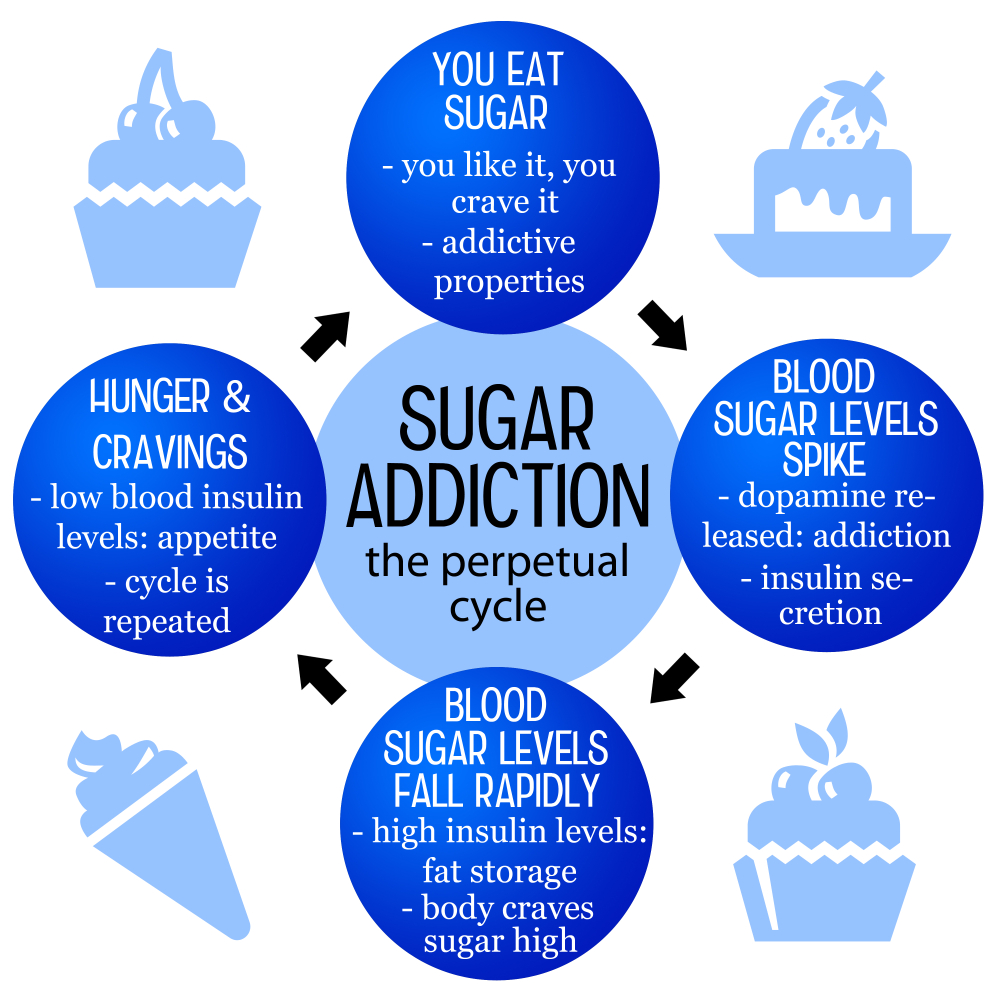
When we talk about sugar addiction, we are venturing into a gray area of nutritional science. Frank Hu, a prominent nutrition researcher, points out that while sugar can increase cravings and create compulsive eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria that substances like alcohol or nicotine do. This distinction is crucial because it indicates that although we may experience a strong desire for sugar-laden treats, the substance itself might not trigger the same biochemical response in the brain as commonly recognized addictive drugs. This leads to the question of whether the addictive qualities of sugar warrant concern, especially in an era where processed food addiction is on the rise.
Understanding sugar addiction involves recognizing how ultra-processed foods affect our bodies. These foods, which are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, significantly enhance palatability and lead to habitual consumption. As a result, many consumers find themselves in a cycle of craving sugary snacks, which can mimic the withdrawal-like symptoms experienced by individuals attempting to quit stronger substances. Therefore, while sugar might not be classified as addictive in the same way as other drugs, its effects on our cravings and eating behaviors can be profound, shaping our food choices and overall health.
The Effects of Sugar on the Body
The effects of sugar on the body extend far beyond mere weight gain. Research suggests that high sugar intake can lead to an increased risk of several metabolic disorders, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. These health issues arise because excessive sugar consumption often leads to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less effective at using insulin. This dysfunction can trigger a cascade of health problems, emphasizing the importance of monitoring sugar intake, particularly from processed food sources, which are notoriously high in added sugars.
Moreover, sugar can significantly impact mental health. Studies indicate that high sugar diets may be correlated with mood swings, anxiety, and even depression. This connection between sugar and emotional well-being stems from fluctuations in blood sugar levels, which can cause feelings of irritability and fatigue. Hence, being mindful of the effects of sugar is vital for both physical and mental health; consuming it in moderation can lead to better overall wellness, reducing the likelihood of sugar-related health issues.
Cravings and Compulsive Eating
Sugar cravings are a common experience for many, often leading to compulsive eating behaviors. These cravings can be particularly intense when consuming sugar-laden foods like candies and baked goods, which are designed to stimulate our taste buds. This creates a cycle where the more sugar we consume, the more we desire these foods, often leading to overeating and poor dietary choices. Acknowledging this cycle is essential, as it can help individuals develop healthier eating habits and make more informed decisions regarding their sugar consumption.
Addressing sugar cravings requires a strategic approach. Professionals often recommend gradually reducing added sugars rather than going ‘cold turkey,’ as this can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms that may discourage individuals from sticking to their healthier eating plans. Instead, by substituting high-sugar snacks with whole fruits or nuts, individuals can satisfy their sweet tooth in a healthier way while also curtailing the compulsions associated with processed foods. Understanding the psychological aspects of cravings can empower individuals to take control of their eating habits.
Processed Food Addiction and Sugar
Processed food addiction is a growing concern in today’s society, primarily because many of these products contain high levels of added sugars designed to enhance flavor and increase consumer appeal. These highly palatable foods can lead to habitual overeating and have been linked to obesity and other health issues. Understanding the addictive qualities of sugar found in these processed foods can help raise awareness about the risks associated with overconsumption and the challenges of breaking free from these dietary patterns.
Furthermore, the immediate satisfaction derived from consuming sugary processed foods can overshadow the longer-term health consequences, contributing to a cycle of addiction. By recognizing that the convenience and taste of these products can lead to unhealthy eating habits, individuals can begin to make more mindful choices. Focusing on whole food alternatives and reducing the reliance on processed items can play a crucial role in reversing the trends of sugar addiction and promoting better health outcomes.
Is Sugar Bad for You?
The question ‘Is sugar bad for you?’ is frequently answered with nuance, as it heavily depends on context and quantity. While sugar itself is necessary for energy, excessive consumption—especially of added sugars found in processed foods—can lead to numerous health issues, from weight gain to metabolic syndrome. Thus, moderation is the key—like many components of a balanced diet, sugar can be part of a healthy lifestyle if consumed wisely.
Health organizations, including the American Heart Association, recommend limits on added sugar intake to help mitigate health risks. For men, this is capped at about 9 teaspoons per day, while women should aim for around 6 teaspoons. Exceeding these amounts can lead to serious health consequences, emphasizing the importance of not only being mindful of how much sugar we consume but also paying attention to its sources and forms in our diets.
The Importance of Label Reading
Reading food labels is paramount in understanding the sugar content in our diets. Many processed foods, including snacks, sauces, and beverages, might not immediately present themselves as high in sugar. Yet, a closer look at nutritional labels can reveal surprising amounts of added sugars that contribute to daily intake, often exceeding recommended limits. By learning to interpret these labels effectively, consumers can make informed decisions about their food and manage their sugar consumption better.
Moreover, being proactive about reading labels enables consumers to identify healthier alternative foods that are lower in added sugars. This practice encourages a more conscious approach to eating, allowing for better control over one’s diet. Incorporating awareness of ingredient lists and sugar content can ultimately lead to significant improvements in overall health and well-being.
Understanding Health Recommendations
Health recommendations regarding sugar intake are based on extensive research linking high consumption to negative health outcomes. Organizations such as the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association provide guidelines intended to help individuals limit their sugar intake for better health. These recommendations typically include not only limits on the amount of added sugar but also encouragement to choose naturally occurring sugars found in whole foods like fruits and vegetables.
Understanding these recommendations and their rationale can empower individuals to make healthier dietary choices. By adhering to the suggested limits and focusing on nutrient-dense, whole-food options, it is possible to enjoy a balanced diet that supports overall health, minimizing the negative effects associated with excessive sugar consumption.
Sugar: A Source of Pleasure, Not Just Cravings
While discussions around sugar frequently focus on the dangers of addiction and compulsive consumption, it is equally important to recognize sugar as a source of enjoyment and pleasure in our diets. Moderation allows for the inclusion of sweet flavors in healthy meals, enhancing not just the taste but overall meal satisfaction. Understanding the role of sugar in life—not just as a potential addictive substance, but also for its contributions to culinary delight—creates a more balanced view of its place in our diets.
This perspective encourages individuals to appreciate sweetness without guilt, fostering a healthier relationship with food. Instead of labeling all sugar as ‘bad,’ recognizing it as part of enjoyable meals can lead to more mindful consumption practices. This nuanced view supports individuals in creating fulfilling and enjoyable eating experiences without falling into the traps of excess or addiction that often accompany processed foods.
Breaking Free from Sugar Cravings
Breaking free from sugar cravings can be a challenging yet rewarding journey. Understanding the immediate effects of sugar on the brain and body can motivate individuals to seek healthier alternatives. Strategies for managing these cravings often include staying hydrated, eating balanced meals rich in fiber and protein, and gradually reducing sugar intake. By doing so, individuals can retrain their palates and reduce their desire for sweet foods over time.
Additionally, creating an environment that supports healthy choices is imperative. Removing ultra-processed foods from the home and replacing them with nutritious snacks can help reduce temptations. Support systems such as friends, family, or community groups can also play a significant role in maintaining commitment to healthier eating habits. Knowing that others are going through similar challenges can provide encouragement and camaraderie in this journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can produce cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it’s not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, its addictive qualities can still lead to withdrawal-like symptoms when consumption is abruptly stopped.
What are the effects of sugar on the brain?
Sugar can activate the brain’s reward system, similar to addictive substances. This can lead to increased cravings and a desire to consume more sugary foods, contributing to what some refer to as sugar addiction.
How does processed food addiction relate to sugar consumption?
Processed foods often contain high levels of added sugar, which can enhance their palatability and lead to habitual consumption. This can create a cycle of cravings and overconsumption, similar to other forms of addiction.
What are sugar cravings, and why do they occur?
Sugar cravings are intense desires for sugary foods that can occur due to changes in blood sugar levels or the addictive qualities of sugar. These cravings can lead to overconsumption and reliance on sugary snacks.
Can sugar be part of a healthy diet without leading to addiction?
Yes, sugar can be included in a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. It’s essential to differentiate between naturally occurring sugars in foods and added sugars in processed products, which should be limited to avoid potential its addictive effects.
What are some strategies to manage sugar cravings and reduce sugar addiction?
Gradually reducing sugar intake instead of going cold turkey can help manage sugar cravings. This can be achieved by reading food labels, choosing whole foods, and replacing sugary snacks with healthier options.
Are there withdrawal symptoms associated with sugar addiction?
Some individuals may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, or anxiety when they cut out sugar abruptly, indicating the potential addictive qualities of sugar.
How can understanding sugar addiction help with dietary changes?
Recognizing the addictive qualities of sugar can encourage individuals to be more mindful of their sugar consumption, making it easier to limit intake and choose healthier food options.
Is it possible to be addicted to sugar without realizing it?
Yes, many people may not recognize their dependency on sugar, as cravings and habitual consumption can develop over time without conscious awareness.
What is the recommended daily limit for added sugar to avoid potential addiction?
The American Heart Association recommends no more than 9 teaspoons of added sugar for men and 6 teaspoons for women daily to minimize the risk of sugar-related health issues and cravings.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, but it isn’t officially classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Withdrawal symptoms from stopping sugar can include headaches, dizziness, and anxiety, though these are less severe than for addictive substances. |
| Intake of sugar in excessive amounts is problematic; moderation is crucial with a recommended limit of 9 teaspoons for men and 6 teaspoons for women. |
| Sugar is present in many essential foods such as fruits and whole grains, distinguishing it from substances that can be completely eliminated from the diet. |
| Gradual reduction of sugar intake is recommended instead of abrupt removal to avoid backlash effects. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The topic sparks a complex discussion concerning cravings and the distinction between necessary food and addictive substances. While sugar may have some addictive qualities, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. It’s essential to moderate sugar intake to maintain a healthy diet, yet we also recognize the enjoyment that comes from sweetness in our meals. Understanding the balance between enjoyment and intake can lead to healthier eating habits without completely eliminating sugar.