Alzheimer’s disease early detection plays a critical role in managing this devastating condition that affects millions worldwide. Innovative research has led to the development of an olfactory test for Alzheimer’s that helps identify those at risk long before they experience any significant symptoms of cognitive decline. This simple at-home Alzheimer’s screening enables individuals to assess their olfactory abilities as a potential early warning sign of neurodegenerative disease. By focusing on subtle changes in scent recognition, researchers are uncovering the vital connection between smell and cognitive impairment. Understanding these signs not only aids in early diagnosis but also paves the way for timely interventions to improve quality of life for those at risk.
The early identification of Alzheimer’s disease can significantly impact individuals and families dealing with this neurological disorder. In recent developments, researchers have explored various methods, including cognitive impairment tests and scent-based assessments, to detect early signs of neurodegenerative diseases. Utilizing an at-home screening, individuals can evaluate their olfactory function, which may serve as an essential indicator of impending cognitive decline. By recognizing subtle symptoms of cognitive impairment, we open pathways for innovative treatment approaches that can alter the course of these conditions. Enhancing detection methods is vital for proactive health management and improving outcomes for those affected.
Understanding the Importance of Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease
Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease can be a game changer in the management and treatment of this neurodegenerative disorder. Identifying cognitive impairment as soon as possible allows for interventions that can slow the progression of symptoms and improve the quality of life. Researchers emphasize that recognizing the signs of cognitive decline early could facilitate timely access to resources, support, and clinical trials, which could ultimately lead to better health outcomes for patients and their families.
With innovative approaches such as at-home screening tests, like olfactory tests, early identification of Alzheimer’s disease is becoming more feasible. These tests, which assess the ability to identify and remember different odors, are designed to be accessible to older adults from the comfort of their homes. Studies have shown that even slight changes in olfactory function can indicate cognitive impairment, making these tests valuable for detecting early signs of Alzheimer’s before other symptoms manifest.
Olfactory Tests as a Reliable Tool for Assessing Cognitive Impairment
Olfactory tests are revealing interesting correlations between sense of smell and cognitive health. Research has shown that older adults with mild cognitive impairment tend to score lower on these tests compared to their cognitively normal peers. This decline in olfactory function may provide clues about the health of the brain and could serve as an early indicator of neurodegenerative disease, particularly Alzheimer’s disease. By integrating olfactory assessments into regular health check-ups, healthcare providers could enhance monitoring for cognitive decline.
As we move towards more personalized medicine, incorporating cognitive impairment tests like olfactory assessments can yield important data for both patients and clinicians. Furthermore, the simplicity of these tests allows for comprehensive screening in diverse populations without the need for complicated equipment or settings. This could empower individuals to take charge of their cognitive health and seek early intervention when necessary.
Exploring the Link Between Smell and Memory Loss
Research indicates a strong link between the senses, particularly smell, and cognitive functions like memory. The olfactory system is closely intertwined with the areas of the brain responsible for memory and emotion, making it a sensitive barometer of cognitive health. As Alzheimer’s disease progresses, many individuals experience alterations in their olfactory function, which can be one of the earliest signs of the disease. Understanding this connection highlights the potential of olfactory tests for early detection of cognitive decline.
Various studies reveal that individuals experiencing cognitive impairment often report changes in their sense of smell. By focusing on olfactory dysfunction, researchers are gaining insights into how early interventions could be targeted. Using odor identification as an assessment tool could potentially help clinicians in designing targeted therapeutic approaches, thereby catching the onset of Alzheimer’s disease before significant cognitive decline occurs.
The Role of At-Home Alzheimer’s Screening in Individual Health Management
At-home Alzheimer’s screening represents a significant advancement in the monitoring of cognitive health, allowing individuals to take proactive steps in their health management. By using tools such as olfactory tests, individuals can assess their cognitive function in a private and comfortable environment. These early assessments pave the way for timely consultations with healthcare providers, which is critical for planning further testing or interventions if needed.
This increased accessibility to screening tools means that a larger segment of the population can engage in monitoring their cognitive health. Particularly for older adults or those living in remote areas, the ability to perform screening tests at home could break down barriers to early detection of Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of cognitive decline. This proactive approach not only alleviates anxiety but also encourages individuals to seek help sooner.
Recognizing Symptoms of Cognitive Decline: A Comprehensive Guide
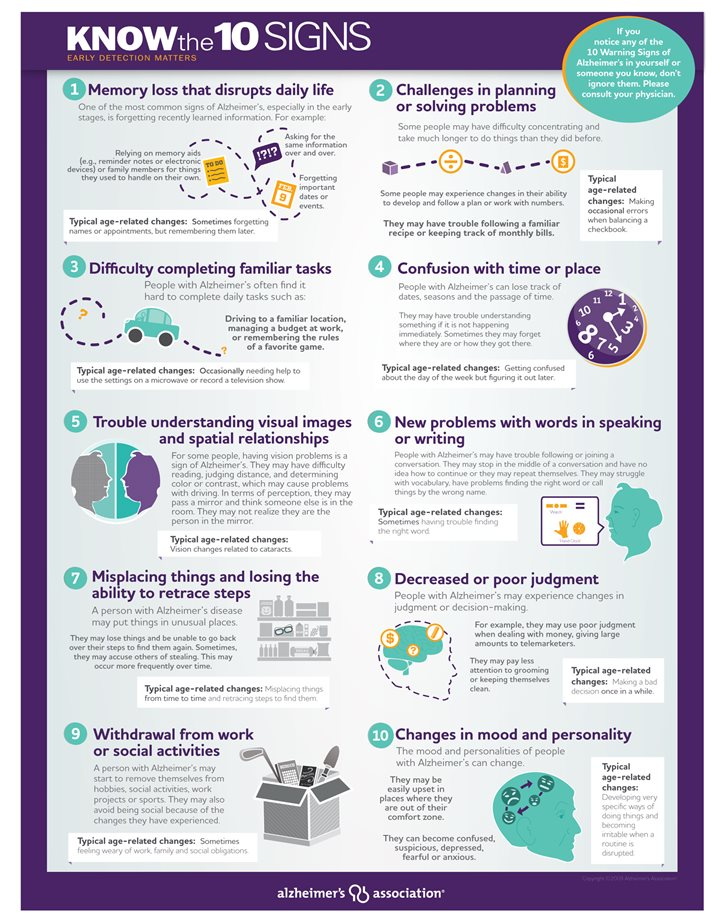
Identifying symptoms of cognitive decline is crucial for early intervention in Alzheimer’s disease. Common signs include forgetfulness, difficulty in completing familiar tasks, trouble recalling names, and changes in mood or personality. Awareness of these symptoms can empower individuals and their families to seek medical advice promptly, potentially leading to early diagnosis and the application of preventative strategies.
Additionally, subtle changes in social interaction and communication can also indicate cognitive decline. Individuals may withdraw from social situations or struggle to follow conversations. Noticing these signs as precursors to more serious cognitive issues highlights the importance of regular cognitive health checks and the potential role of at-home testing as an early detection method.
Future Directions in Alzheimer’s Research and Testing Approaches
The future of Alzheimer’s research is promising, particularly with the development of multifunctional testing approaches and innovative screening methods. As studies continue to validate at-home olfactory tests, researchers aim to enhance the reliability of these tools for broader clinical use. Future directions may also involve integrating these tests with other cognitive assessments, thereby creating a comprehensive profile of an individual’s cognitive health.
Moreover, ongoing research is expected to establish guidelines for when and how often these screening tests should be administered, considering variables such as age and family history. This multifaceted approach to Alzheimer’s disease detection and management is essential for developing effective prevention strategies and ultimately improving patient care.
The Impact of Neurodegenerative Disease Signs Beyond Alzheimer’s
Neurodegenerative disease signs extend beyond Alzheimer’s and can encompass a variety of disorders, including Parkinson’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Recognizing the overlapping symptoms—such as motor function changes and cognitive decline—can facilitate a more accurate assessment and timely care. The integration of olfactory and cognitive tests could provide crucial information needed for distinguishing among these disorders.
By understanding the broader spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases, healthcare providers can develop more comprehensive diagnostic and treatment pathways. This holistic view not only aids in identifying specific conditions but also emphasizes the importance of early detection and intervention across various cognitive disorders, improving overall treatment outcomes.
The Importance of Professional Guidance in Alzheimer’s Testing
While at-home Alzheimer’s screening tools like olfactory tests are gaining popularity, it’s important to interpret the results with professional guidance. Healthcare providers can help contextualize test scores within an individual’s broader health picture and recommend appropriate next steps, whether that be further testing or lifestyle interventions. Such collaboration is essential for effective cognitive health management.
Professional involvement in the testing process emphasizes the need for accuracy and thoroughness. Misinterpretation of test results can lead to unnecessary anxiety or delayed treatment, which could have severe implications for individuals at risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Engaging healthcare professionals ensures that individuals receive appropriate care based on reliable evaluations.
Community Awareness and Education on Alzheimer’s Disease
Community awareness and education play a vital role in addressing Alzheimer’s disease effectively. Initiatives that promote understanding of cognitive impairment symptoms and the significance of early detection can empower the public to take informed actions regarding their health. Educational campaigns can dispel myths about Alzheimer’s and encourage conversations around mental health in older adults.
Strategies to foster community engagement include workshops, informative brochures, and accessible presentations, which can help raise awareness about at-home Alzheimer’s screening tools and their importance. Engaging communities fosters a culture of proactive health management, making it easier for individuals to seek assistance whenever signs of cognitive decline appear.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the role of olfactory tests in Alzheimer’s disease early detection?
Olfactory tests are designed to evaluate a person’s ability to identify and remember odors, which can serve as an early detection tool for Alzheimer’s disease. Research indicates that older adults with cognitive impairment often struggle with these tests, showing that a decline in the sense of smell may signal early neurodegenerative disease signs.
How can at-home Alzheimer’s screening help in early detection?
At-home Alzheimer’s screening, such as the olfactory test developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, allows individuals to assess their risk of cognitive impairment conveniently. This testing method helps identify potential signs of Alzheimer’s disease before significant symptoms of cognitive decline occur, enabling earlier interventions.
What are the symptoms of cognitive decline that might indicate Alzheimer’s disease?
Symptoms of cognitive decline that may indicate Alzheimer’s disease include memory loss, difficulty with problem-solving, challenges in learning new information, and impairment in smell perception as assessed through olfactory tests. Recognizing these signs early is crucial for timely diagnosis and management.
What are some cognitive impairment tests available for early detection of Alzheimer’s?
Cognitive impairment tests, such as olfactory tests for Alzheimer’s, are becoming vital for early detection. These tests focus on assessing olfactory dysfunction, which has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases and can help identify at-risk individuals long before major symptoms develop.
How do olfactory dysfunction and Alzheimer’s disease relate?
Olfactory dysfunction, characterized by a diminished sense of smell, has been identified as an early warning sign for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Research shows that individuals with cognitive impairment score lower on olfactory tests, making it a viable method for early detection of Alzheimer’s.
| Key Points |
|---|
| Researchers from Mass General Brigham developed an at-home olfactory test to identify Alzheimer’s risk years before symptoms. |
| The test involves participants smelling odor labels and assessing their ability to identify and remember them. |
| Older adults with cognitive impairment perform worse on this test compared to cognitively normal adults. |
| The goal is to create a cost-effective, non-invasive test to detect Alzheimer’s early and intervene sooner. |
| The research shows that olfactory dysfunction may indicate early signs of neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Future studies may link olfactory testing with neuropsychological assessments to track cognitive decline more accurately. |
Summary
Alzheimer’s disease early detection is crucial for identifying individuals at risk many years before the onset of memory loss symptoms. Recent research indicates that olfactory testing—assessing an individual’s ability to identify and remember odors—could serve as an effective early indicator of cognitive decline. By developing non-invasive, cost-effective at-home tests, researchers aim to facilitate early interventions and contribute to advancements in treatment and research for Alzheimer’s disease. Monitoring olfactory function may not only help detect Alzheimer’s more effectively but also shed light on other neurodegenerative diseases, enhancing our ability to combat these conditions as they arise.